Canadian Mortgage Rates: Higher Soon, How High?
A normal English article with predictions of Canadian Mortgage Interest Rate Predictions, September 2021.
We think these rates are going to happen but ON A LONGER TIME RANGE that what they think.
Summary of Expected Rates*
- 2.55% – 2.65% in October, 2021
- 2.60% – 2.85% in December, 2021, reduction in buying power of 7%
- 3.10% – 3.30% in October, 2021, reduction in buying power of 8% – 14%
*These rates can totally happen, and are still lower than Pre-Covid rates, but also consider these things that would delay economic recovery/ keep rates low: Iraq – any thing, a 4th and 5th wave of Covid, new variants, USA droughts/ wild weather.
Mortgage Mark Herman, top Calgary Alberta mortgage broker, for new buyers
And a Renewal Surprise:
You may be surprised by the cost of a renewal. A $500,000 mortgage with a 5-year fixed rate of 2.0% would pay around $46,080 in interest over the term. If that rises to 3.1% next year, the cost of interest over the same period would be $72,183. That is an extra $26,000 if interest a year. ANSWER: look at renewing early. We can help you out with that.
OK … on with the news:
The Canadian economy is improving, excluding some minor hiccups like this morning’s GDP. An improved economy needs less stimulus, and that means higher mortgage rates. To see what Canada is in for, we modeled a forecast range for 5-year fixed-rate mortgages. If Canada doesn’t go into a double-dip recession, much higher mortgage rates are coming.
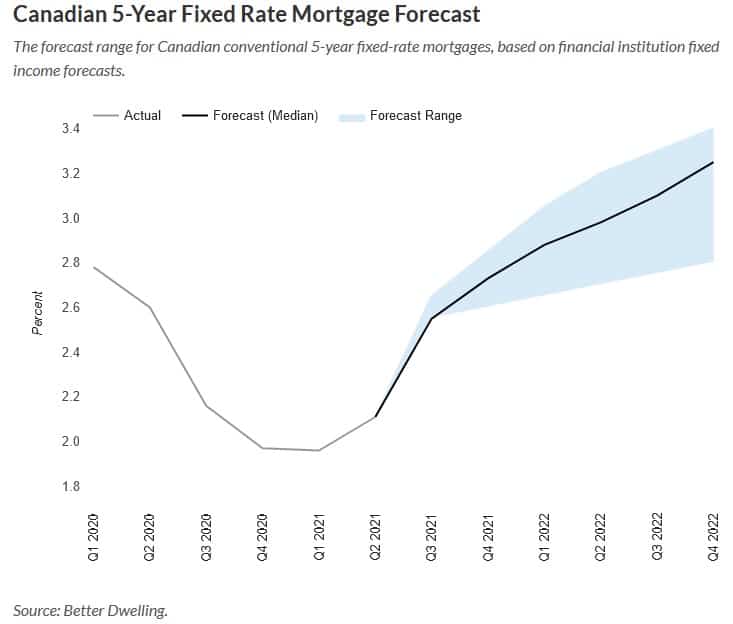
Canadian 5 Year Fixed-Rate Mortgage Forecast
Today we’re looking at 5-year fixed-rate mortgage interest, and where it’s heading. More specifically, we’ll be focusing on conventional (aka uninsured) mortgage rates. These are for homeowners with a decent amount of equity, and a loan to value ratio below 80%. Insured and variable rate mortgages follow a different path. However, they’ll generally follow the same trend.
This model is based on fixed income forecasts created by major financial institutions. Since they’re forecasting how much investors will make, we can forecast how much you’ll pay. Just a couple of quick notes for the nerds, and aspiring nerds.
The strength of the economy and the recovery are going to be big factors in determining how high these go. A stronger economy means a faster recovery, and along with that is higher mortgage rates. Weaker economic performance will generally mean lower rates to stimulate borrowing. As economic conditions change, so will these forecasts.
Credit liquidity will also play a role in the direction of mortgage rates. If there’s excess capital to lend, mortgage lenders tend to accept smaller margins. This helps to lower the cost of borrowing since they’ll make it up on revenue. If capital for mortgages becomes scarce, mortgage rates rise to adjust to demand.
Today’s chart assumes a medium level of credit liquidity. That is, not much excess, but it’s not scarce either. That’s how the mortgage market was pre-pandemic, and we’ll assume it goes back to that.
Canadian Mortgage Rates Are Going To Climb
Mortgage borrowing costs are likely to reach pre-pandemic levels soon. Our median 5-year fixed-rate forecast is 2.55% by the end of Q3 2021. Based on the most bullish yield forecast, it would rise to 2.65%. The downside yield forecast is the same as the median.
Most institutions have consistent near-term expectations. That sounds weird, but it makes sense. Near-term forecasts are the most visible, with the least number of variables compounding. As forecasts are further out, we’ll see the gap widen as their difference in outlook is magnified.
Canadian 5-Year Fixed Rate Mortgage Forecast
The forecast range for Canadian conventional 5-year fixed-rate mortgages, based on financial institution fixed income forecasts.
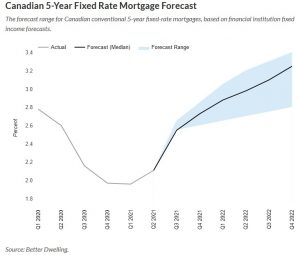
Mortgage Interest Rates Can Increase Substantially By Year-End
By the end of this year, we start to really see the potential for these rates to climb. By Q4 2021, the median forecast would put a typical 5-year fixed-rate mortgage at 2.73%. The forecast range becomes wider, going from 2.6% (low) to 2.85% (high). It may not sound like much, but it can have a big impact.
The rate of change is much more important than the actual number. If you go from a 2% rate to a 2.73% rate, your cost of interest rises 36.5%. If we exclude the stress test, buying power sees a 7.84% decline. Since recent buyers are mostly stress-tested, default isn’t much of an issue. However, the cost and size of debt can be.
Mortgages Rates May Rise More Than A Point By Next Year
Next year is going to be a big one for mortgage rates if the economy recovers as expected. The median 5-year fixed-rate forecast works out to 3.10% by the end of Q3 2022, which can lead to an 11.5% reduction in buying power. On the low end, the rate still comes in at 2.7%, reducing buying power by 8.0% outside of a stress test. The high range would see it climb all the way to 3.30%, pulling maximum mortgage credit 14.3% lower. Keep in mind the stress test rate may also adjust higher as well. It depends on how comfortable OSFI is with rates rising closer to their stress test number.
Another factor to consider here is the cost of the renewal. A $500,000 mortgage with a 5-year fixed rate of 2.0% would pay around $46,080 in interest over the term. If that rises to 3.1% next year, the cost of interest over the same period would be $72,183. I don’t know about you, but $26,000 is a decent chunk of money to spend over a year.
Existing mortgage holders close to renewal may want to text their mortgage broker. If you see the economy improving, locking in rates might save you a little money. It might not though, depending on whether you have prepayment penalties. It’s always best to run the numbers with a broker on various scenarios though.
Pending a double-dip recession doesn’t occur, higher mortgage rates are coming. Maybe not as high as the Desjardins forecast, but definitely higher than it is now. Those supersized mortgages with short terms are going to divert more capital from the economy on renewal. The takeaway isn’t how high mortgage rates can climb though. It’s how absurdly cheap mortgage debt has been during the pandemic.
Link to the actual article: https://betterdwelling.com/canadian-mortgage-rates-will-rip-higher-soon-heres-how-high/#_
EXPLAINER: Why & Where Inflation and Canadian Mortgage Interest Rates

Best answer I have seen yet is below … it still makes the 5-year fixed the better option right now (for most people)Mortgage Mark Herman, Top Calgary Mortgage Broker
The latest significant news was good, but modest. Canada’s unemployment rate dipped to 7.5% with the creation of 94,000 jobs in July. Most of those are full-time and in the private sector.
Employment levels are linked to inflation, which is a key factor watched by the Bank of Canada in setting interest rate policy which, in turn, can affect mortgage rates.
As the labour market tightens up, employers tend to offer higher wages to attract workers. That increases the cost of producing goods and services, driving inflation. As well, as more people get work and earn more money demand for goods and services increases. If that demand outpaces supply, inflation can also result.
Canada finds itself in this position now. Inflation is running high chiefly because of supply constraints caused by the pandemic. At the same time, more and more people are heading back to work.
That has some analysts forecasting the Bank of Canada will be raising rates to calm inflation. The Bank, however, has been saying otherwise.
It is also useful to watch what is happening in the United States. The two economies are tightly linked and actions in the U.S. can offer useful clues about what will happen here.
In its latest assessment of the American economy the U.S. Federal Reserve continued to down play inflation – which is running high there as well – as “transitory”. The Fed continues to look to the second half of 2023 as the most likely time for any possible rate hikes. While the Bank of Canada has said it expects rates could start rising as much as a year sooner than that, it would be unusual for the BoC to move before the Fed.