Probably the end of Mortgage Rate Reductions for Canada
Expert opinions on Bank of Canada interest rate cuts are shifting. A growing number of market watchers are backing away from their predictions of two more reductions this year. Several are now saying the Bank has likely reached the end of the current trimming cycle.
Back in April we said that Prime is probably going to stay where it is now; discounting the expected 4 more reduction to 0.
that looks to have come true.
5-year fixed is the way to go to side-step all the world’s recent happenings .
Mortgage Mark Herman, best Calgary mortgage broker near me.
The central bank held its trend-setting Policy Rate at 2.75% for a second time in its decision on June 4. Since then, inflation numbers and Gross Domestic Product readings have given the BoC reasonable grounds to stand pat.
Statistics Canada’s latest figures for GDP show it declined by 0.1% in April compared to March. Much of that decline was led by the manufacturing sector, which is falling victim to U.S. tariffs and trade uncertainty. A similar reduction is forecast for May. While many economists admit the slowdown shows the economy is softening, they say it is not on the verge of collapse. GDP is 1.3% higher that it was a year earlier.
The other key factor in the Bank’s rate decisions, inflation, held steady at 1.7% in May. That headline number is actually below the Bank’s target of 2.0% and would normally suggest there is room for a further rate cut. However, that is a little deceiving.
Headline inflation (aka the Consumer Price Index) continued to be skewed by the elimination of the consumer carbon tax. As well, core inflation, which is the BoC’s preferred measure, remains stuck at 3.0%, which is the high end of the Bank’s desired inflation range.
The Bank finds itself trying to balance economic growth against the risk of rising inflation. The Bank’s next interest rate announcement is set for July 30.
Canadian Mortgage Economic Data, June 4th, 2025
The Bank of Canada announced today that it is keeping its benchmark interest rate at 2.75%, unchanged from April (and March) of 2025.
As noted under “Rationale”, the Bank appears to be in a holding pattern until it gains more information on the direction of US trade policy and its impact on Canada.
Below, is a summary of the Bank’s observations and its outlook.
Summary – the 5-year fixed is the best option for June 2025 and July 2025 so far. ensure you get a rate hold are rates are creeping up.
Mortgage Mark Herman, top Calgary Mortgage Broker for First Time Buyers
Canadian Economic Performance, Housing, Employment and Outlook
- Economic growth in the first quarter came in at 2.2%, slightly stronger than the Bank had forecast, while the composition of GDP growth was largely as expected
- The pull-forward of exports to the United States and inventory accumulation boosted activity, with final domestic demand “roughly flat”
- Strong spending on machinery and equipment held up growth in business investment by more than expected
- Consumption slowed from its very strong fourth-quarter pace, but continued to grow despite “a large drop” in consumer confidence
- Housing activity was down, driven by a sharp contraction in resales; government spending also declined
- The labour market has weakened, particularly in trade-intensive sectors, and unemployment has risen to 6.9%
- The economy is expected to be considerably weaker in the second quarter, with strength in exports and inventories reversing and final domestic demand remaining subdued
Canadian Inflation
- Inflation eased to 1.7% in April, with the elimination of the federal consumer carbon tax shaving 0.6 percentage points off the Consumer Price Index
- Excluding taxes, inflation rose 2.3% in April, slightly stronger than the Bank had expected
- The Bank’s preferred measures of core inflation, as well as other measures of underlying inflation, moved up
- Recent surveys indicate that households continue to expect that tariffs will raise prices and many businesses say they intend to pass on the costs of higher tariffs
- The Bank will be watching all of these indicators closely to gauge how inflationary pressures are evolving
Global Economic Performance
- While the global economy has shown resilience in recent months, this partly reflects a temporary surge in activity to get ahead of tariffs
- In the United States, domestic demand remained relatively strong but higher imports pulled down first-quarter GDP
- US inflation has ticked down but remains above 2%, with the price effects of tariffs still to come
- In Europe, economic growth has been supported by exports, while defence spending is set to increase
- China’s economy has slowed as the effects of past fiscal support fade; more recently, high tariffs have begun to curtail Chinese exports to the US
- Since financial market turmoil in April, risk assets have largely recovered and volatility has diminished, although markets remain sensitive to US policy announcements
- Oil prices have fluctuated but remain close to their levels at the time of the April Monetary Policy Report
Rationale
With uncertainty about US tariffs still high, the Canadian economy softer but not sharply weaker, and some unexpected firmness in recent inflation data, the Bank’s Governing Council decided to hold the policy rate steady “as we gain more information on US trade policy and its impacts.
Looking Ahead: Uncertainty Remains High
The Bank noted that since its April Monetary Policy Report, the US administration has continued to increase and decrease various tariffs. China and the United States have stepped back from extremely high tariffs and bilateral trade negotiations have begun with a number of countries. However, the Bank said the outcomes of these negotiations “are highly uncertain,” tariff rates are well above their levels at the beginning of 2025, and new trade actions are still being threatened. Uncertainty remains high.
As a result, the Bank says it is proceeding carefully, with particular attention to the risks and uncertainties facing the Canadian economy. These include: the extent to which higher US tariffs reduce demand for Canadian exports; how much this spills over into business investment, employment and household spending; how much and how quickly cost increases are passed on to consumer prices; and how inflation expectations evolve.
Final comments
Today’s announcement ended with the following statement from the Bank’s Governing Council: “We are focused on ensuring that Canadians continue to have confidence in price stability through this period of global upheaval. We will support economic growth while ensuring inflation remains well controlled.”
Next scheduled BoC rate announcement
The Bank is scheduled to make its fifth policy interest rate decision of 2025 on July 9th.
BMO & CIBC: Not on list of Top-11 banks in Canada
Wow hey??
Who would guess that 2 of Big-6 banks that millions of Canadians “think they have a financial relationship with” did not even make the list of the Top-11 banks in Canada.
It is surprising the amount of customers that call us looking to “beat their bank’s mortgage rate” when they should be looking at if they should even be doing mortgage business at their main personal bank.
Mortgage Mark Herman, Calgary Alberta new home buyer and mortgage renewal specialist of 21 years.
We recommend that they also look at the T’s & C’s – Terms and Conditions – to their own bank’s mortgages to find:
- Payout penalties that are 500% to 800% – yes, 5x to 8x the amount of payout penalties at broker banks.
- Their renewal rates are usually always at rates higher than what Broker Banks offer – because Broker Banks know the broker that placed you there will jump at the chance to move them to a different bank, for a better/ market rate, and then we get paid again. Big-6 banks don’t have to worry about that because you are usually not aware of market rates.
- SELF-employed mortgage holders are often “worked over by the Big-6 banks” whereas, Broker Banks are more than happy doing tons for self-employed business owners.
Here’s the full list of Canada’s best banks for 2025, according to Forbes:
- Tangerine
- Simplii Financial
- RBC
- PC Financial
- Vancity
- EQ Bank
- TD
- Scotiabank
- National Bank
- Desjardins
- ATB Financial
footnote: link action here https://www.narcity.com/best-banks-in-canada-forbes-2025
RBC Mortgage Payout Penalties Skyrocket in 2025
Details of the recent actions RBC has taken to INCREASE THE PAYOUT PENALTY for their own customers.It shows that Big-6 Banks are not your best -mortgage- friend. Brokers Are!Mortgage Mark Herman, Top Calgary Alberta mortgage broker
If you’re seeking a textbook case of banks giving consumers the short end of the stick, look no further.
The nation’s biggest mortgage lender, RBC, just slashed its posted rates.
“RBC’s move is the biggest move to increase penalties (IRDs) since its posted rates peaked on September 20, 2023,” says Matt Imhoff, founder of Prepayment Penalty Mentor.
For those fluent in the dark arts of interest rate differential (IRD) charges, this spells disaster for anyone daring to escape their RBC mortgage shackles early. Here’s precisely how grim it gets…
This is what RBC did to its posted rates today (Friday):
- 5 Year: -30 bps
- 4 Year: -25 bps
- 3 Year: -35 bps
- 2 Year: -85 bps
- 1 Year: -55 bps
- 6 Month: -55 bps
Anyone attempting to break a 2, 5, 7, or 10-year RBC mortgage now is potentially in for a world of penalty hurt due to these changes.
By way of example, if you’re an originator poaching a $500,000 RBC 4.4% 3-year fixed originated in July 2024, that client would be staring down a penalty of approximately $17,500, Imhoff says.
That’s up almost $10,000 in one day—simply because RBC slashed the comparison rate (its 2-year posted rate in this case).
In other words, the 255 bps “discount” from posted that this customer got in 2024 is now like a financial boomerang, coming back to hit them hard Imhoff says.
“This IRD is significantly higher than it should be, and that’s the risk of going with a bank where posted rates are elevated.”
In the above example, the client’s only option to avoid more than a three-month interest penalty would be to ride out their RBC term until they have just 1.41 years remaining (per the chart below).
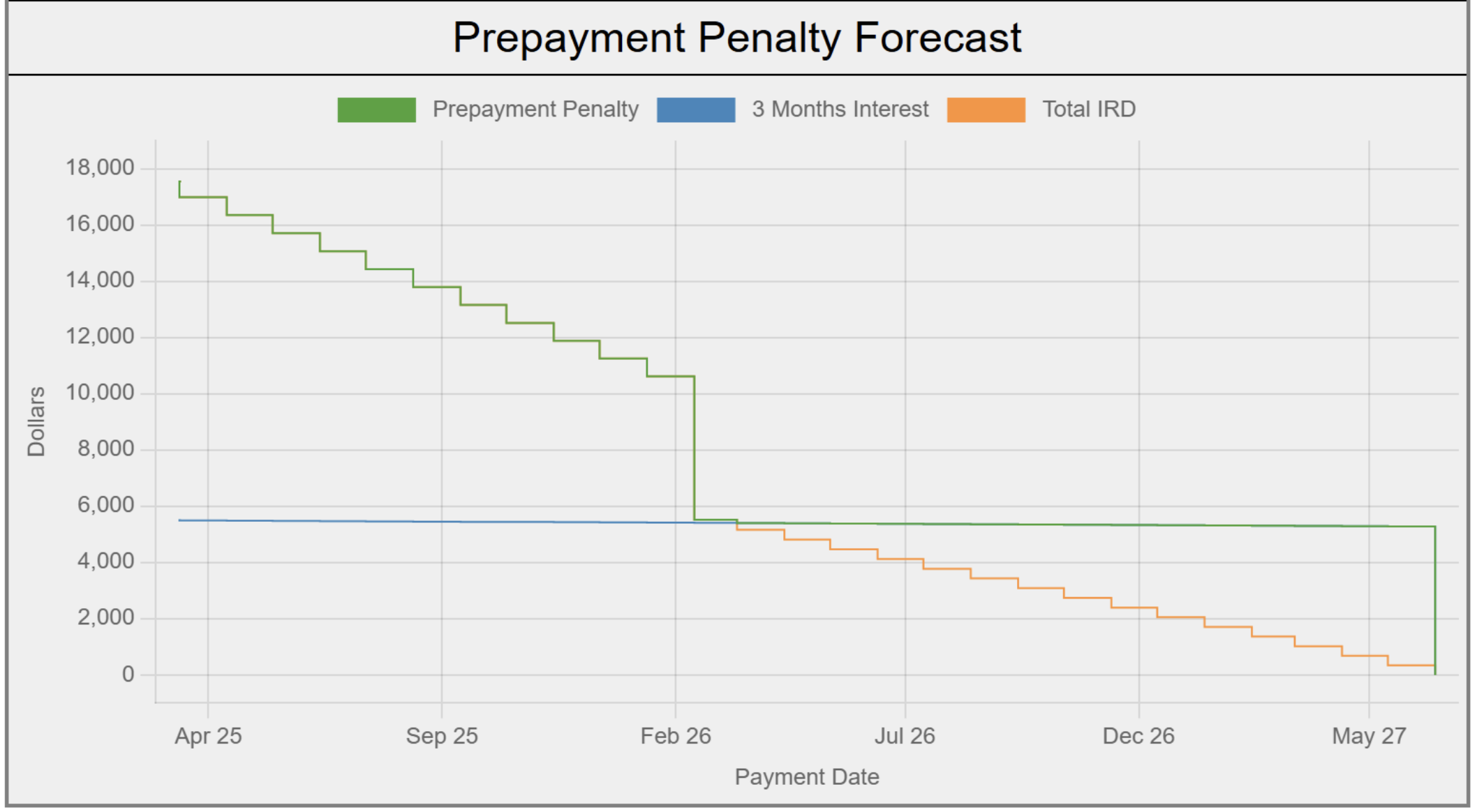
To virtually ensure a three-month interest penalty, a customer needs to be just eight months shy of their mortgage’s maturity, as illustrated in the RBC table below.
Watch out for TD customers
As Matt’s table below shows, TD’s posted rates are well above where they typically reside relative to bond yields. As a result, “I believe this sets the stage for what TD will inevitably do,” he says.
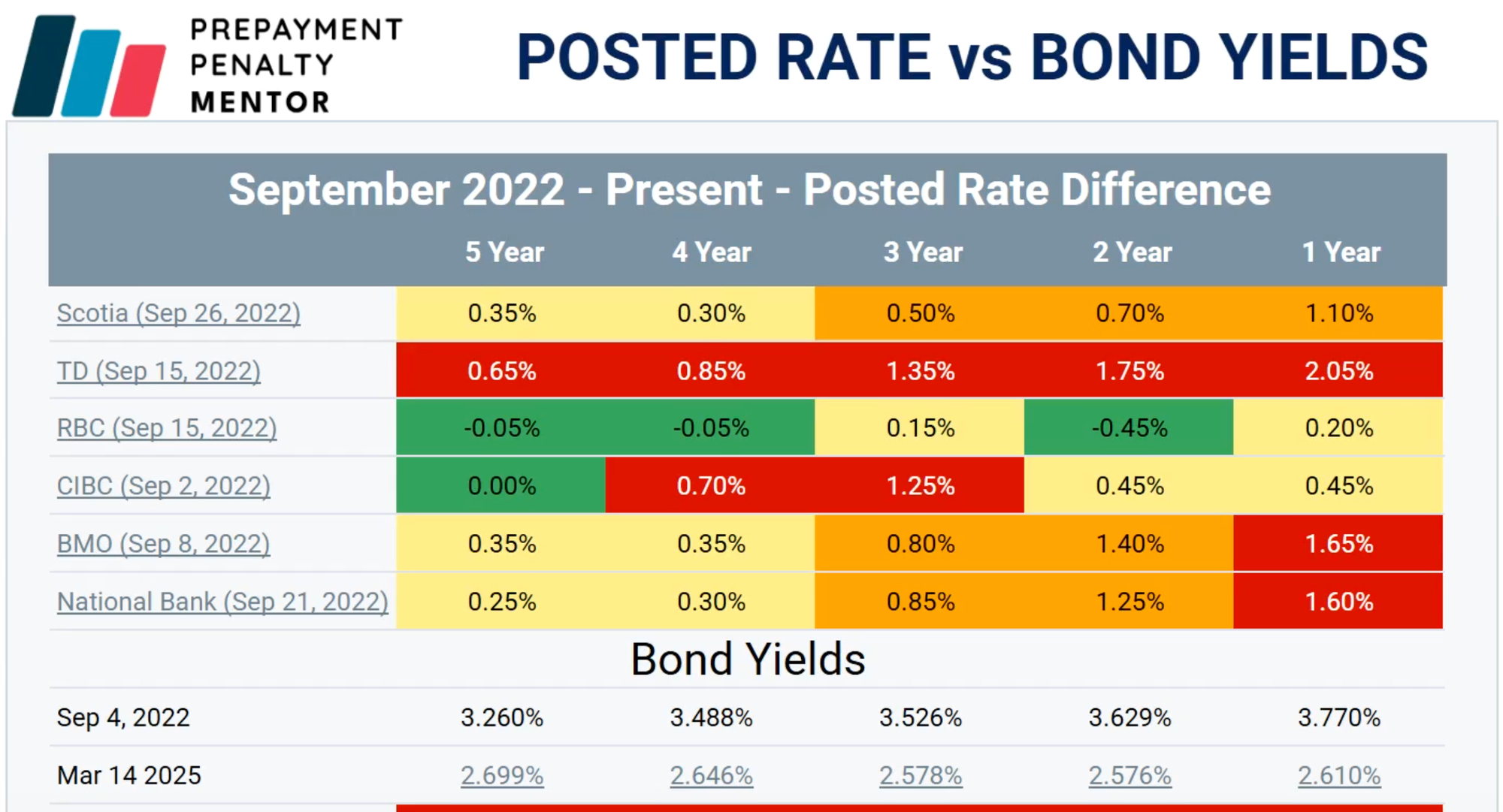
In cases where a client needs to refi, he adds that the risk of imminent posted rate changes at TD makes it too risky for brokers to get the deal approved elsewhere and then request discharge from TD. Time is money in this case.
“If a broker tries to get a payout order from TD today, TD can wait up to five business days,” Imhoff notes, adding that during that time, the penalty can go up.
In the event that early discharge makes clear sense, he says, “I am advising brokers to have their TD clients go to the branch, break the mortgage, pay the penalty while it is still on sale, and switch into an open.”
PPM has a great table (below) that also shows which terms at which banks are most prone to IRD penalties. Terms in red face IRD charges now, based on the assumptions the user enters. Terms in orange are at risk of being charged IRDs on the next posted rate drop.
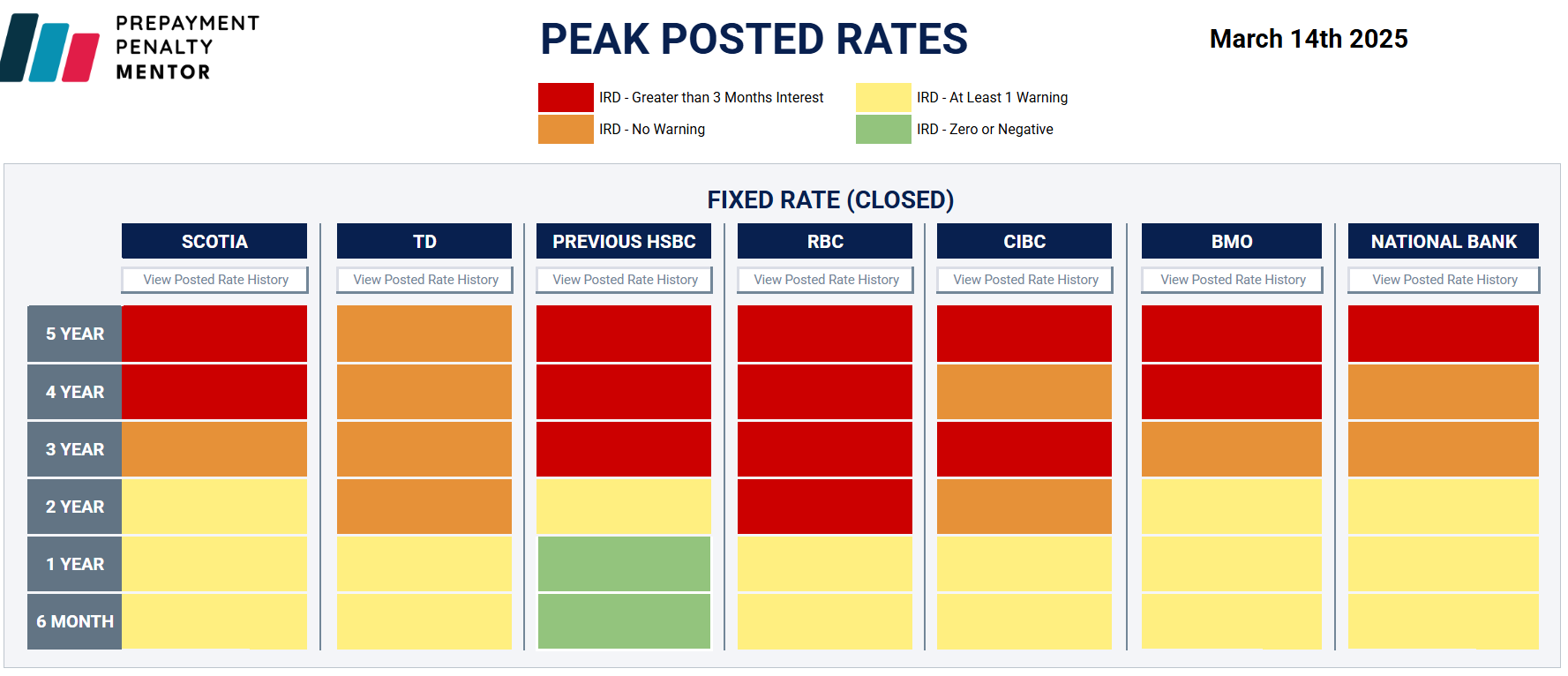
It pays to know in advance when penalties make a refinance uneconomical. “There are brokers working on deals today that will never fund—all that wasted time, effort, money, just to get a payout that kills the deal.”
Bank of Canada lowers benchmark interest rate to 3%
The Bank of Canada opened its monetary policy playbook for 2025 with a 0.25% reduction in its overnight rate. The 6th since June of last year.
In issuing its January Monetary Policy Report, the Bank also noted that its projections are subject to “more-than-usual uncertainty” because of the rapidly evolving policy landscape, particularly the threat of trade tariffs by the new administration in the United States.
Variable rates win, but can you handle some possibly sleepless nights if Trump’s tariffs increase fixed rates as much as 3%?
(Click to see the link to the report showing this.)
If Canada does a full retaliation to Trump’s 25% tariffs our Canadian interest rates could go up by 3%; and if there is no retaliation at all, Canadian interest rates could go down by up to 3% as well!
Mortgage Mark Herman, 20+ years of mortgage experience with an MBA from a top school & Top Calgary Alberta Mortgage Broker
Below, we summarize the Bank’s commentary.
Canadian economic performance and housing
- Past interest rate reductions have started to boost the Canadian economy
- Recent strengthening in both consumption and housing activity is expected to continue
- Business investment, however, remains weak
- The outlook for exports is supported by new export capacity for oil and gas
Canadian inflation and outlook
- Inflation measured by the Consumer Price Index (CPI) remains close to 2%, with some volatility due to the temporary suspension of the GST/HST on some consumer products
- Shelter price inflation is still elevated but it is easing gradually, as expected
- A broad range of indicators, including surveys of inflation expectations and the distribution of price changes among components of the CPI, suggest that underlying inflation is close to 2%
- The Bank forecasts CPI inflation will be around the 2% target over the next two years
Canadian labour market
- Canada’s labour market remains soft, with the unemployment rate at 6.7% in December
- Job growth, however, has strengthened in recent months, after lagging growth in the labour force for more than a year
- Wage pressures, which have proven sticky, are showing some signs of easing
Global economic performance, bond yields and the Canadian dollar
- The global economy is expected to continue growing by about 3% over the next two years
- Growth in the United States has been revised upward, mainly due to stronger consumption
- Growth in the euro area is likely to be subdued as the region copes with competitiveness pressures
- In China, recent policy actions are boosting demand and supporting near-term growth, although structural challenges remain
- Since October, financial conditions have diverged across countries with bond yields rising in the US, supported by strong growth and more persistent inflation, and bond yields in Canada down slightly
- The Canadian dollar has depreciated materially against the US dollar, largely reflecting trade uncertainty and broader strength in the US currency
- Oil prices have been volatile and in recent weeks have been about $5 higher than was assumed in the Bank’s October Monetary Policy Report
Other comments
The Bank also announced its plan to complete the normalization of its balance sheet, which puts an end to quantitative tightening. The Bank said it will restart asset purchases in early March 2025, beginning gradually so that its balance sheet stabilizes and then grows modestly, in line with growth in the economy.
It also offered further rationale for today’s decisions by saying that with inflation around 2% and the economy in excess supply, the Bank’s Governing Council decided to reduce its policy rate. It also noted that cumulative reduction in the policy rate since last June is “substantial.” Lower interest rates are boosting household spending and, in the outlook it published (see below), the economy is expected to strengthen gradually and inflation to stay close to target.
Outlook
In today’s announcement, the Bank laid out its forecast for Canadian GDP growth to strengthen in 2025. However, it was quick to also point out that with slower population growth because of reduced immigration targets, both GDP and potential growth will be “more moderate” than what the Bank previously forecast in October 2024.
To put numbers on that forecast, the Bank now projects GDP will grow by 1.8% in both 2025 and 2026. As a result, excess supply in the Canadian economy is expected to be “gradually absorbed” over the Bank’s projection horizon.
Setting aside threatened US tariffs, the Bank reasons that the upside and downside risks in its outlook are “reasonably balanced.” However, it also acknowledged that a protracted trade conflict would most likely lead to weaker GDP and higher prices in Canada and test the resilience of Canada’s economy.
The Bank ended its statement with its usual refrain: it is committed to maintaining price stability for Canadians.
2025 will bring more BoC news
The Bank is scheduled to make its second policy interest rate decision of 2025 on March 12th. I will provide an executive summary immediately following that announcement.
Prime to be 2% LOWER in 15 months, Dates of drops, Variable rate wins: Fall 2024
Yes, with the writing on the wall for the coming Prime rate decreases the Variable rate is the way to go.
Variable rates are based on Consumer Prime, which moves the exact same as the Bank of Canada’s “overnight rate.” The decreases in the overnight rate will be the same for Consumer Prime and they are below.
So Sept 4, 2024, Prime will go from 6.7% to 6.45%
Canadian Consumer Prime – what Variable Rates are based on – will be these rates here.
If your “discount is Prime – 0.95%” then your rate would be this number below – 0.95%. And as you can see, this is way better than the 3-year fixed at 4.84% or the 5- year fixed at 4.69% today.
- September 4, 2024: 6.45%
- October 23, 2024: 6.20%
- December 11, 2024: 5.95%
- January 2025: 5.70%
- March 2025: 5.45%
- April 2025: 5.20%
- June 2025: 4.95%
- September 2025: 4.70%
- October 2025: 4.45%
- December 2025: 4.20%
Article is here: Bank of Canada’s policy interest rate could dip to 2.75% by late 2025:
forecast:: https://dailyhive.com/vancouver/bank-of-canada-policy-interest-rate-forecast-2025-credit-1
Predictions of the article for the rate drops: Credit 1’s Bank of Canada policy interest rate forecast, as updated on August 26, 2024:
-
- September 4, 2024: 4.25%
- October 23, 2024: 4.0%
- December 11, 2024: 3.75%
- January 2025: 3.5%
- March 2025: 3.5%
- April 2025: 3.25%
- June 2025: 3.25%
- September 2025: 3.0%
- October 2025: 2.75%
- December 2025: 2.75%
Bank of Canada Leaves Prime the Same, April 2024
As Expected, No change in Bank of Canada benchmark interest rate for April 2024.
As noted in August 2023, the 1st Prime Rate reduction is expected in July and then Prime should come down at o.25% every 90 days so … 1 quarter percent reduction, every calandar quarter, for the next 2 years.
Mortgage Mark Herman, best top Calgary Alberta mortgage broker.
Today, the Bank of Canada announced it is keeping its benchmark interest rate at 5.0%, unchanged from July of 2023. However, much has changed in the economy and in the world since then. For evidence, we parsed today’s announcement and present a summary of the Bank’s key observations below.
Canadian Inflation
- CPI inflation slowed to 2.8% in February, with easing in price pressures becoming more broad-based across goods and services. However, shelter price inflation is still very elevated, driven by growth in rent and mortgage interest costs
- Core measures of inflation, which had been running around 3.5%, slowed to just over 3% in February, and 3-month annualized rates are suggesting downward momentum
- The Bank expects CPI inflation to be close to 3% during the first half of 2024, move below 2.5% in the second half, and reach the 2% inflation target in 2025
Canadian Economic Performance and Housing
- Economic growth stalled in the second half of last year and the economy moved into excess supply
- A broad range of indicators suggest that labour market conditions continue to ease. Employment has been growing more slowly than the working-age population and the unemployment rate has risen gradually, reaching 6.1% in March. There are some recent signs that wage pressures are moderating
- Economic growth is forecast to pick up in 2024. This largely reflects both strong population growth and a recovery in spending by households
- Residential investment is strengthening, responding to continued robust demand for housing
- The contribution to growth from spending by governments has also increased. Business investment is projected to recover gradually after considerable weakness in the second half of last year. The Bank expects exports to continue to grow solidly through 2024
- Overall, the Bank forecasts GDP growth of 1.5% in 2024, 2.2% in 2025, and 1.9% in 2026. The strengthening economy will gradually absorb excess supply through 2025 and into 2026
Global Economic Performance and Bond Yields
- The Bank expects the global economy to continue growing at a rate of about 3%, with inflation in most advanced economies easing gradually
- The US economy has “again proven stronger than anticipated, buoyed by resilient consumption and robust business and government spending.” US GDP growth is expected to slow in the second half of this year, but remain stronger than forecast in January
- The euro area is projected to gradually recover from current weak growth. Global oil prices have moved up, averaging about $5 higher than the Bank assumed in its January Monetary Policy Report
- Since January, bond yields have increased but, with narrower corporate credit spreads and sharply higher equity markets, overall financial conditions have eased
- The Bank has revised up its forecast for global GDP growth to 2.75% in 2024 and about 3% in 2025 and 2026
- Inflation continues to slow across most advanced economies, although progress will likely be bumpy. Inflation rates are projected to reach central bank targets in 2025
Outlook
Based on the outlook, Governing Council said it decided to hold the Bank’s policy rate at 5% and to continue to “normalize” the Bank’s balance sheet. It also noted that while inflation is still too high and risks remain, CPI and core inflation have eased further in recent months.
The Council said it will be looking for evidence that this downward momentum is sustained. Governing Council is particularly watching the “evolution of core inflation,” and continues to focus on the balance between demand and supply in the economy, inflation expectations, wage growth, and corporate pricing behaviour.
As it has said consistently over the past year, the Bank will remain “resolute in its commitment to restoring price stability for Canadians.”
Next Touchpoint
On June 5th, 2024, the Bank returns with another monetary policy announcement and economists are already lining up with predictions of a rate cut either then or in July.
Net Migration to Alberta – #’s here.
the CORE reason home prices in Calgary will be going up for the next 4 years, and are 100% supported and will not be coming down is summed up in this article right here.
https://www.cbc.ca/news/canada/calgary/alberta-population-records-2023-to-2024-data-1.7157110
Summary of the Main Reasons Home Prices are Supported:
- BC and Ontario home prices are DOUBLE Calgary home prices
- 4 million New Canadians on the way here in the next 5 years.
- We hatched the largest 20 – 29 year old population Canada has EVER had, and they are moving out of their parent’s basements and buying their own homes.
- Alberta does NOT have PST
- Alberta does not have a 1% “welcome to the neighborhood tax” when buying property.
After researching the above data points we can confidently say all 5 of these stacked factors will cause home prices to increase is all price ranges for the next few years.
Mortgage Mark Herman, licensed as a top Alberta Mortgage Broker for 21 years and 1 year in BC
Using Business Income / Corporate Income to Qualify for a Mortgage in Canada, 2024
Are you self- employed and thinking about, or hopping to use your own business income or corporate income to help you qualify for a mortgage?
It is possible, but not very common, as it usually does not help as much as we hope it would.
Mortgage Mark Herman, best Calgary Alberta mortgage broker for self-employed buyers
For RESIDENTIAL Purposes:
Very few lenders (like 3 out of 40+) will consider using business income that is not on personal taxes.
- When they will allow the business income added in, they only use between 40-60% of the net business income after dividends paid.
- They wouldn’t allow the operating company to actually be on mortgage/title;
- it would be in personal name or
- Hold Co name (with full personal guarantee, for the full mortgage amount – with full recourse. Meaning they can/ do/ will sue you into bankruptcy if they need to foreclose.)
Docs Needed
They do need to review more data than usual if trying to use business financials. I addition to the regular documents needed (2 years of T1 Generals, and NOAs and T4’s if there is T4 income), add in these docs:
For the Business:
- 2 years of professional accountant prepared financial statements
- including a signed ‘Notice to Reader’ and
- Need a compilation of all billing engagements for the fiscal periods
Catch – there are always a few:
If the property in question has a large shop – it is usually not allowed in determining the value so a higher mortgage amount is usually required.
They also have a hard time if there is any income to be derived from the property.
Acreage Details
Max land is limited to 4, 8, or 10 acres – depending on lender
- Only the home, de/attached garage and 4 acres are used for valuation by lender.
- NO value is attributed to: out-buildings, sheds, riding rings, stables, storage, nor fences
- Many of which could be valued at 200k+, like fences and buildings.
The End of Prime Rate Increases, January, 2024, Canada
Horray, today The Bank of Canada didn’t just put rate hikes on the back burner today; it unplugged the stove!
The Bank is now “confident enough” that inflation is on the right track to not publicly dwell on rate hike risk any longer. That was today’s message from Senior Deputy Governor Carolyn Rogers after the BoC left its overnight rate at 5%.
Instead, the Bank says it’s now shifting its focus to “how long” the overnight rate needs to marinate “at the current level.”
Summary:
No more increases to the Canadian Prime Rate of Interest – at 7.2% today, after 10 increases in 2023.
Back in August I said Prime should start to come down in June – still the best guess – and
will come down by o.25% every 3 months, so one-quarter-percent decrease every calendar / fiscal quarter (3 months)
for a total of 2% less than today so … Prime should end up at 5.2% in 30 months, which is June 2026.
Mortgage Mark Herman, top Calgary Alberta and BC mortgage broker
“We need to give these higher interest rates time to do their work,” Macklem said, offering no clues on how long he’ll let the rate hike stew simmer. The forward market thinks it’ll take another 4 – 6 months. Historically, rates have plateaued at peak levels for anywhere from a few months to 17 months. So far, it’s been only 6.
The Bank says that higher rates can’t be completely ruled out, but it’s very rare for the Bank of Canada to hike a bunch, pause 5+ months, hike more, pause 5+ months more, and then hike again.
