Current Risks to the Canadian Mortgage Market? May 15th, 2024
Summary:
May 21, 2024 is when the inflation a report comes out and it should be the determining factor if the Canadian PRIME RATE of INTEREST is reduced from 7.2% in June or not. Maybe July. Maybe later.
Nobody is buying anything big right now, which is the idea … to reduce inflation.
Which means now is the best time to buy a home before everyone waiting for rates to drop jumps in on the 1st Prime rate reduction.
Says Mortgage Mark Herman, Calgary Alberta best/ top/ mortgage broker for first time home buyers
DATA:
Mortgage holders have been anxiously waiting for the Bank of Canada to cut interest rates. The increase of 90,400 jobs in April – 5 times what analysts expected – has heightened concerns that the Bank will continue to wait before lowering rates. 🙁
While the economy has not slowed as much as expected, there’s growing economic slack, with the jobless rate up 1 percentage point over the past year and a 24% year-over-year increase in the number of unemployed individuals, which is slowing down wage growth. The crucial factor in determining whether a rate cut will occur in June or be postponed to later this year hinges on the April CPI release scheduled for May 21st.
In the background of these deliberations, the Bank of Canada also assesses various potential risks to the economy. Last week, the Bank released its Financial Stability Report, highlighting two key risks: debt serviceability and asset valuations.
The report notes that the share of mortgage holders who are behind on their credit cards and auto loan payments, which had hit historic lows during the pandemic, has now returned to more normal levels. It also notes that smaller mortgage lenders are seeing an uptick in credit arrears. This increase isn’t surprising, given the run up in rates and the market segment that these lenders cater to. While the arrears rate is up, it remains relatively low compared to historical levels.
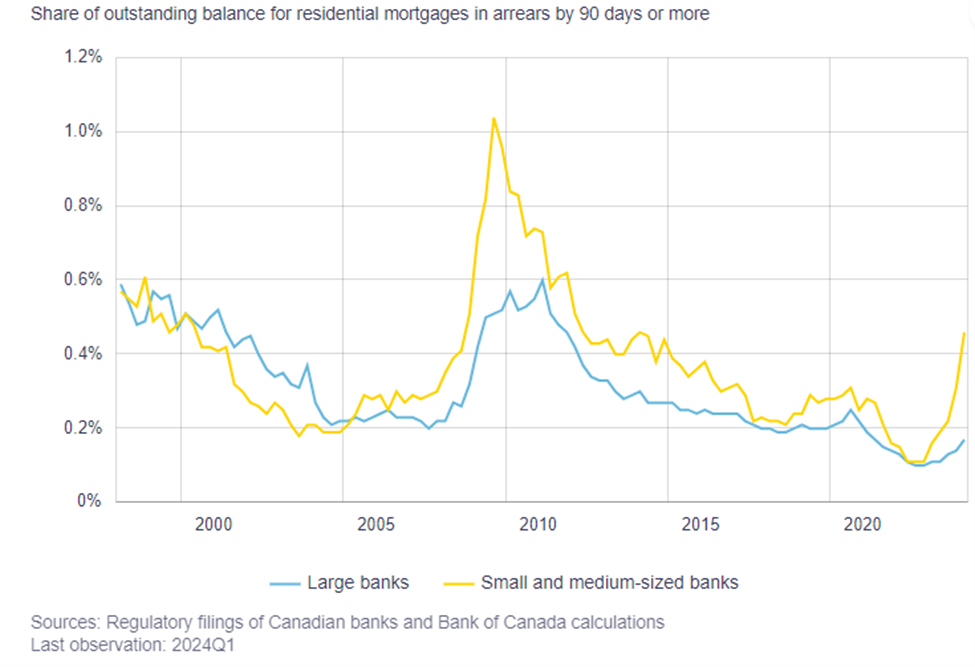
This overall positive portfolio performance is due to two key factors: 1) financial flexibility and 2) employment.
Canadian mortgage defaults tend to spike up during periods of rising unemployment. While the unemployment rate has risen, it remains relatively low. Additionally, mortgagors are holding higher levels of liquid assets. Before the pandemic, homeowners with a mortgage held 1.2 months of liquid reserves, which increased to 2.2 months during the pandemic and has since fallen to 1.8 months. These increased reserves provide a solid buffer for mortgagors to meet unexpected increases in expenses.
The Bank remains concerned that nearly half of all outstanding mortgages have yet to be renewed, leaving these borrowers at risk of payment shock due to the increase in interest rates. Scotiabank is an interesting case because, unlike other banks, it offers adjustable-rate mortgages (ARM) with variable payments instead of variable rate mortgages with fixed payments. Scotia has seen its 90+ days past due rate increase from 0.09% to 0.16%. During their fourth-quarter earnings call, Scotia noted that ARM borrowers have been cutting back on discretionary spending by 11% year-over-year, compared to a 5% reduction among fixed-rate clients.
The mortgage maturity profile in the Financial Stability Report suggests that we could see significant slowing in consumer discretionary spending over the next two years. While the rise in debt-servicing costs will be partially offset by income growth, we should expect to see belt tightening by mortgage holders. This poses less of a risk to the banking sector mortgage market than to the overall outlook for the economy.
