Prime now 6.95% from 7.20%: BoC reduces its benchmark interest rate to 4.75%
Today, the Bank of Canada reduced its overnight policy interest rate by 0.25% to 4.75%. This welcome and widely expected decision comes on the heels of evidence pointing to a deceleration of the rate of inflation.
SUMMARY:
The “overnight rate” being quoted is the rate that Banks borrow from each other at, not consumer Prime, which is confusing.
Canadian Consumer Prime has just been reduced from 7.20% to 6.95% – this only affects Variable Rate mortgages.
Fixed rates remain unchanged because they track the Canadian Mortgage Bond Rates which are different, and similar.
There has also been about 40 “silent” fixed rate reductions of o.o5% each in 2024 that the press did not cover.
Mortgage Mark Herman, Top best Calgary Alberta mortgage broker specializing in 1st time buyers
Below we examine the Bank’s rationale for this move by summarizing its observations below, including its all-important outlook comments that are sure to shape market expectations for the remainder of the year.
Canadian inflation
- Inflation measured by the Consumer Price Index (CPI) eased further in April to 2.7%
- The Bank’s preferred measures of core inflation also slowed and three-month indicators suggest continued downward momentum
- Indicators of the breadth of price increases across components of the CPI have moved down further and are near their historical average, however, shelter price inflation remains high
Canadian economic performance and housing
- Economic growth resumed in the first quarter of 2024 after stalling in the second half of last year
- At 1.7%, first-quarter GDP growth was slower than the Bank previously forecast with weaker inventory investment dampening activity
- Consumption growth was solid at about 3%, and business investment and housing activity also increased
- Labour market data show Canadian businesses continue to hire, although employment has been growing at a slower pace than the working-age population
- Wage pressures remain but look to be moderating gradually
- Overall, recent data suggest the economy is still operating in excess supply
Global economic performance and bond yields
- The global economy grew by about 3% in the first quarter of 2024, broadly in line with the Bank’s April Monetary Policy Report projection
- The U.S. economy expanded more slowly than was expected, as weakness in exports and inventories weighed on activity
- In the euro area, activity picked up in the first quarter of 2024 while China’s economy was also stronger in the first quarter, buoyed by exports and industrial production, although domestic demand remained weak
- Inflation in most advanced economies continues to ease, although progress towards price stability is “bumpy” and is proceeding at different speeds across regions
- Oil prices have averaged close to the Bank’s assumptions, and financial conditions are little changed since April
Summary comments and outlook
The Bank cited continued evidence that underlying inflation is easing for its decision to change its policy interest rate. More specifically, it said that “monetary policy no longer needs to be as restrictive.”
Also welcome was the Bank’s statement that “recent data” have “increased our confidence that inflation will continue to move towards” its 2% target.
However, it also added this to its outlook: “Nonetheless, risks to the inflation outlook remain. Governing Council is closely watching the evolution of core inflation and remains particularly focused on the balance between demand and supply in the economy, inflation expectations, wage growth, and corporate pricing behaviour.”
And has it has been doing for some time, it said the Bank “remains resolute in its commitment to restoring price stability for Canadians.”
Next up
The Bank returns on July 24th with its next monetary policy announcement – I think they will do another 0.25% reduction at the next meeting and they will continue to reduce at every meeting for the next 3 meetings this year.
Current Risks to the Canadian Mortgage Market? May 15th, 2024
Summary:
May 21, 2024 is when the inflation a report comes out and it should be the determining factor if the Canadian PRIME RATE of INTEREST is reduced from 7.2% in June or not. Maybe July. Maybe later.
Nobody is buying anything big right now, which is the idea … to reduce inflation.
Which means now is the best time to buy a home before everyone waiting for rates to drop jumps in on the 1st Prime rate reduction.
Says Mortgage Mark Herman, Calgary Alberta best/ top/ mortgage broker for first time home buyers
DATA:
Mortgage holders have been anxiously waiting for the Bank of Canada to cut interest rates. The increase of 90,400 jobs in April – 5 times what analysts expected – has heightened concerns that the Bank will continue to wait before lowering rates. 🙁
While the economy has not slowed as much as expected, there’s growing economic slack, with the jobless rate up 1 percentage point over the past year and a 24% year-over-year increase in the number of unemployed individuals, which is slowing down wage growth. The crucial factor in determining whether a rate cut will occur in June or be postponed to later this year hinges on the April CPI release scheduled for May 21st.
In the background of these deliberations, the Bank of Canada also assesses various potential risks to the economy. Last week, the Bank released its Financial Stability Report, highlighting two key risks: debt serviceability and asset valuations.
The report notes that the share of mortgage holders who are behind on their credit cards and auto loan payments, which had hit historic lows during the pandemic, has now returned to more normal levels. It also notes that smaller mortgage lenders are seeing an uptick in credit arrears. This increase isn’t surprising, given the run up in rates and the market segment that these lenders cater to. While the arrears rate is up, it remains relatively low compared to historical levels.
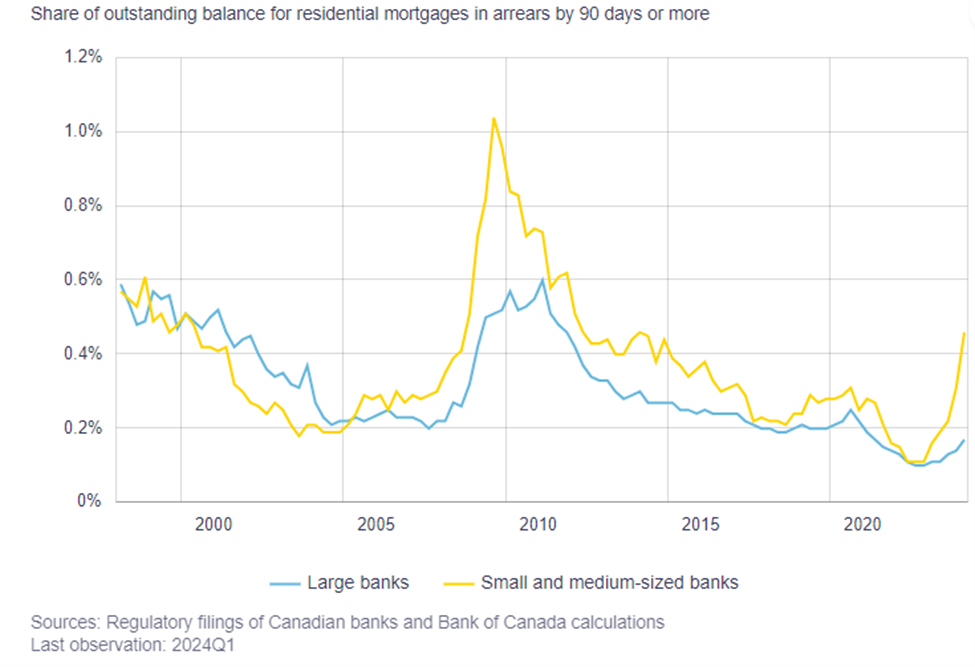
This overall positive portfolio performance is due to two key factors: 1) financial flexibility and 2) employment.
Canadian mortgage defaults tend to spike up during periods of rising unemployment. While the unemployment rate has risen, it remains relatively low. Additionally, mortgagors are holding higher levels of liquid assets. Before the pandemic, homeowners with a mortgage held 1.2 months of liquid reserves, which increased to 2.2 months during the pandemic and has since fallen to 1.8 months. These increased reserves provide a solid buffer for mortgagors to meet unexpected increases in expenses.
The Bank remains concerned that nearly half of all outstanding mortgages have yet to be renewed, leaving these borrowers at risk of payment shock due to the increase in interest rates. Scotiabank is an interesting case because, unlike other banks, it offers adjustable-rate mortgages (ARM) with variable payments instead of variable rate mortgages with fixed payments. Scotia has seen its 90+ days past due rate increase from 0.09% to 0.16%. During their fourth-quarter earnings call, Scotia noted that ARM borrowers have been cutting back on discretionary spending by 11% year-over-year, compared to a 5% reduction among fixed-rate clients.
The mortgage maturity profile in the Financial Stability Report suggests that we could see significant slowing in consumer discretionary spending over the next two years. While the rise in debt-servicing costs will be partially offset by income growth, we should expect to see belt tightening by mortgage holders. This poses less of a risk to the banking sector mortgage market than to the overall outlook for the economy.
Net Migration to Alberta – #’s here.
the CORE reason home prices in Calgary will be going up for the next 4 years, and are 100% supported and will not be coming down is summed up in this article right here.
https://www.cbc.ca/news/canada/calgary/alberta-population-records-2023-to-2024-data-1.7157110
Summary of the Main Reasons Home Prices are Supported:
- BC and Ontario home prices are DOUBLE Calgary home prices
- 4 million New Canadians on the way here in the next 5 years.
- We hatched the largest 20 – 29 year old population Canada has EVER had, and they are moving out of their parent’s basements and buying their own homes.
- Alberta does NOT have PST
- Alberta does not have a 1% “welcome to the neighborhood tax” when buying property.
After researching the above data points we can confidently say all 5 of these stacked factors will cause home prices to increase is all price ranges for the next few years.
Mortgage Mark Herman, licensed as a top Alberta Mortgage Broker for 21 years and 1 year in BC
Using Business Income / Corporate Income to Qualify for a Mortgage in Canada, 2024
Are you self- employed and thinking about, or hopping to use your own business income or corporate income to help you qualify for a mortgage?
It is possible, but not very common, as it usually does not help as much as we hope it would.
Mortgage Mark Herman, best Calgary Alberta mortgage broker for self-employed buyers
For RESIDENTIAL Purposes:
Very few lenders (like 3 out of 40+) will consider using business income that is not on personal taxes.
- When they will allow the business income added in, they only use between 40-60% of the net business income after dividends paid.
- They wouldn’t allow the operating company to actually be on mortgage/title;
- it would be in personal name or
- Hold Co name (with full personal guarantee, for the full mortgage amount – with full recourse. Meaning they can/ do/ will sue you into bankruptcy if they need to foreclose.)
Docs Needed
They do need to review more data than usual if trying to use business financials. I addition to the regular documents needed (2 years of T1 Generals, and NOAs and T4’s if there is T4 income), add in these docs:
For the Business:
- 2 years of professional accountant prepared financial statements
- including a signed ‘Notice to Reader’ and
- Need a compilation of all billing engagements for the fiscal periods
Catch – there are always a few:
If the property in question has a large shop – it is usually not allowed in determining the value so a higher mortgage amount is usually required.
They also have a hard time if there is any income to be derived from the property.
Acreage Details
Max land is limited to 4, 8, or 10 acres – depending on lender
- Only the home, de/attached garage and 4 acres are used for valuation by lender.
- NO value is attributed to: out-buildings, sheds, riding rings, stables, storage, nor fences
- Many of which could be valued at 200k+, like fences and buildings.
Updated: Using Disability Income to Qualify for a Canadian Mortgage: 2024
NOTE: this post has been updated in August 2024.
CAN DISABILITY INCOME BE USED TO QUALIFY FOR A CANADIAN MORTGAGE?
YES, it is possible to use disability income to qualify for a pre-approval or a full mortgage approval.
IMPORTANT:
We are ONLY able to use disability income AS A “TOP UP” WHEN YOU ARE BUYING WITH ANOTHER PERSON
- who has standard/ T4 employment income OR qualifies as SELF-EMPLOYED
- AND your file needs more income to “top-up” the qualification amount to get to your target mortgage amount.
Unfortunately, we are not able to use:
- Disability income where it is more than 50% of the income needed to qualify for the mortgage.
- AISH income – the lenders deem provincial supplements as to “risky” and only use “federal programs.”
- If either of these are your situation, we recommend going to an ATB Branch, not online but a BRANCH.
Below are a few clarifications on the typical disability incomes that the banks can use.
- Not all banks accept all types of disability income so we use a few different lenders to ensure we have all your bases covered.
NEXT STEP
Call or send me an email with your contact data so we can have a chat on the phone if you are needing to use a “TOP-UP” via disability income for your purchase.
- I answer from 9-9 x 363, am in the office from 10 – 6:30 most days, best time to call is between 11 am – 3 pm.
- No need to pre-book, just call!
- (How different is that?)
Long-term & Short-term Disability Pension/Insurance
If the borrower has a non-taxable income, the Bank, CMHC and Sagen allow the income to be grossed-up.
- Less than $30,000, this income may be increased by 25%
- At least $30,000, this income may be increased by 35%
Long-term disability: 100% of long-term disability income can be used.
Provide one of the following:
- Letter from the organization or from QPP confirming long-term or permanent disability. If the letter is outdated (over 120 days), current bank statements confirming the deposits are being made to the borrower’s account are also needed
- T4A(P) confirming disability income.
Short-term disability: 100% of the employment income can be used for short-term disability.
Provide the following:
- A letter from the employer confirming the borrower’s return date, position and salary with a verbal confirmation from the employer to ensure the date on the letter is correct. If the return date cannot be confirmed, the disability income can be used for qualifications.
Pension & Retirement Income/Life Annuity
Retirement pensions are fixed incomes, CPP (Canada Pension Plan), OAS (Old Age Security), GIS (Guaranteed Income Supplement), provincial pension plans and private/corporate pensions and must be Canadian pension and evident on Canadian tax return.
IF you are Splitting Retirement Income: In the case where the pension income is shared for tax purposes, the transferring spouse/common-law partner must be on file and only the amount that has not been transferred/split is admissible.
Provide the most recent two documents of the following depending on the source of the declared retirement income:
- Most recent NOA supported by T1 General
- RL-2 Slip
- T4A, T4A(P)
- Letter from the initiating party confirming the yearly pension amount
- Letter from the organization confirming income and permanency of income
- Copy of current bank statement showing the automatic deposit
- Copy of current monthly cheque stub
For CPP, OAS, QPP and GIS, only one relevant document for each source is required from the list above.
RRIF
Income from a RRIF is admissible if there is proof that the portfolio generates a sustainable income amount for the length of the term.
This is a tough one to nail down as the portfolio has to be sustainable and not “drained” over the term of the loan, as in, there will still be a substantial balance in 5 years, if the mortgage is a 5-year term.
Provide the following:
- The most recent NOA supported by T1 General
- Recent RRIF statement to show that the borrower has sufficient assets to support the indicated income for the length of the term
First Nations
This is a non-taxable income. The income can be grossed-up as follows:
- Less than $30,000, this income may be increased by 25%
- At least $30,000, this income may be increased by 35%
Provide the following:
- Copy of the status card needed.
“We use disability income all the time in our practice to top-up mortgage amounts and have access to the banks and lenders that allow it’s use.
Mortgage Mark Herman, top Calgary Alberta and BC mortgage broker, for 21 years.
Canadian Mortgage Data – Nov 14
There has been a little relief for mortgage shoppers in recent days.
- Fixed-rates have come down slightly, led by declining yields for government bonds.
- Variable-rate mortgages appear to be maintaining their discounts and most market watchers believe the Bank of Canada has reached the top of this rate-hiking cycle.
The Bank, however, continues to warn that Canadians should be preparing for interest rates to remain higher for longer. Senior Deputy Governor Carolyn Rogers made that point again during a recent speech in Vancouver, saying it is important to adjust proactively to that possibility. Rogers cited a number of global considerations for higher rates including: China and other developing nations joining the worldwide economy; a decline in attractive investment opportunities for businesses; and an overall, international, adjustment to higher rates.
It is also useful to remember that central banks around the world have been working to normalize interest rates that have been at historic lows since the 2008 financial crisis.
Rogers offered some reassurance that Canadians are adjusting to higher rates. Household credit growth has dropped to its slowest pace since the early ’90s. Delinquency rates on credit cards and other consumer loans are only slightly above pre-pandemic levels. Mortgage delinquencies are below pre-pandemic levels, and that is despite about 40% of all mortgage holders having already renewed at higher rates, with bigger payments.
As to when interest rates might actually start falling? The BoC’s Q3 survey of “Market Participants” suggests they are adjusting to the higher-for-longer scenario. Based on the median response they are expecting a quarter point drop in April, 2024. That is a month later than expectations expressed in the Bank’s Q2 survey.
Finally some good news for buyers.
Buy soon before everyone that did not buy sees this data and tries to by tool
Mortgage Mark Herman – top, best Calgary mortgage broker
Winning Variable Rate Strategy: end-2023
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Canadian Economic Forecast – Nov- Mortgage related use
Bank of Canada holds its interest rate steady, publishes updated economic forecasts

On October 25th, the Bank of Canada announced that it would maintain its Canadian Prime Rate stays at 7.3% – stating that there is “growing evidence” that past interest rate increases are dampening economic activity and relieving price pressures.
This decision provides some comfort to borrowers who have seen their mortgage costs rise steadily since March of 2022. As for real relief – in the form of rate cuts – the Bank demurred, noting that its preferred measures of core inflation show “little downward momentum.” Consequently, the Bank said it is holding this policy rate and continuing its current policy of quantitative tightening.
We capture the Bank’s observations and its latest economic forecasts in the summary below.
Inflation facts and outlook
- In Canada, inflation measured by the Consumer Price Index (“CPI”) has been volatile in recent months: 2.8% in June, 4.0% in August, and 3.8% in September
- Higher interest rates are moderating inflation in many goods that people buy on credit, and this is spreading to services
- Food inflation is easing from very high rates; however, in addition to elevated mortgage interest costs, inflation in rent and other housing costs remains high
- Near-term inflation expectations and corporate pricing behavior are normalizing only gradually, and wages are still growing around 4% to 5%
- The Bank’s preferred measures of core inflation show little downward momentum
Canadian housing and economic performance
- There is growing evidence that past interest rate increases are dampening economic activity and relieving price pressures
- Consumption has been subdued, with softer demand for housing, durable goods and many services
- Weaker demand and higher borrowing costs are weighing on business investment
- A surge in Canada’s population is easing labour market pressures in some sectors while adding to housing demand and consumption
- In the labour market, recent job gains have been below labour force growth and job vacancies have continued to ease; however, the labour market remains “on the tight side” and wage pressures persist
- Overall, a range of indicators suggest that supply and demand in the economy are now “approaching balance”
Global economic performance and outlook
- The global economy is slowing and growth is forecast to moderate further as past increases in policy interest rates and the recent surge in global bond yields weigh on demand
- The Bank projects global GDP growth of 2.9% this year, 2.3% in 2024 and 2.6% in 2025. While this outlook is little changed from the Bank’s July Monetary Policy Report, the composition has shifted, with the US economy proving stronger and economic activity in China weaker than expected
- Growth in the Euro area has “slowed further”
- Inflation has been easing in most economies, as supply bottlenecks resolve and weaker demand relieves price pressures but underlying inflation is persisting, meaning central banks must “continue to be vigilant”
- Oil prices are higher than the BoC assumed in July, and the war in Israel and Gaza is a new source of geopolitical uncertainty
Summary and Outlook
The BoC noted that after averaging 1% over the past year, economic growth is expected to remain “weak” for the next year before increasing in late 2024 and through 2025. Near-term weakness in growth reflects both the broadening impact of past increases in interest rates and slower foreign demand. The subsequent economic “pickup” will be driven by household spending as well as stronger exports and business investment in response to improving fore
ign demand. Spending by governments contributes materially to growth over the forecast horizon. Overall, the Bank expects the Canadian economy to grow by 1.2% this year, 0.9% in 2024 and 2.5% in 2025.
In the Bank’s October projection, CPI inflation is expected to average about 3.5% through the middle of next year before gradually easing to 2% in 2025. Inflation is expected to return to the Bank’s target about the same time as policymakers forecast in their July 2023 projection, “but the near-term path is higher because of energy prices and ongoing persistence in core inflation.”
As for what to expect going forward, the Bank had this to say about interest rates: “With clearer signs that monetary policy is moderating spending and relieving price pressures, Governing Council decided to hold the policy rate at 5% and to continue to normalize the Bank’s balance sheet. However, Governing Council is concerned that progress towards price stability is slow and inflationary risks have increased, and is prepared to raise the policy rate further if needed.”
The message is therefore clear: the Bank wants to see downward momentum in core inflation before it changes tack, and continues to be focused on the “balance between demand and supply in the economy, inflation expectations, wage growth and corporate pricing behaviour.”
Once again, the Bank ended its communique with a familiar phrase: it remains “resolute in its commitment to restoring price stability for Canadians.”
What’s next?
The Bank’s final (scheduled) interest rate announcement of 2023 takes place December 6th and we will follow immediately after with our next executive summary.
Persistent inflation leads the Bank of Canada to increase benchmark interest rate
UGH! The BoC whacks borrowers again.
Mark Herman, Top Calgary Alberta Mortgage Broker
Yesterday, the Bank of Canada increased its overnight interest rate to 5.00% (+0.25% from June) because of the “accumulation of evidence” that excess demand and elevated core inflation are both proving more persistent and after taking into account its “revised outlook for economic activity and inflation.”
This decision was not unexpected by analysts but is disconcerting – as is the Bank’s pledge to continue its policy of quantitative tightening.
To understand today’s decision and the Bank’s current thinking on inflation, interest rates and the economy, we highlight its latest observations below:
Inflation facts and outlook
- In Canada, Consumer Price Index (CPI) inflation eased to 3.4% in May, a “substantial and welcome drop from its peak of 8.1% last summer”
- While CPI inflation has come down largely as expected so far this year, the downward momentum has come more from lower energy prices, and less from an easing of “underlying inflation”
- With the large price increases of last year removed from the annual data, there will be less near-term “downward momentum” in CPI inflation
- Moreover, with three-month rates of core inflation running around 3.5% to 4% since last September, “underlying price pressures appear to be more persistent than anticipated”, an outcome that is reinforced by the Bank’s business surveys, which found businesses are “still increasing their prices more frequently than normal”
- Global inflation is easing, with lower energy prices and a decline in goods price inflation; however, robust demand and tight labour markets are causing persistent inflationary pressures in services
Canadian housing and economic performance
- Canada’s economy has been stronger than expected, with more momentum in demand
- Consumption growth was “surprisingly strong” at 5.8% in the first quarter
- While the Bank expects consumer spending to slow in response to the cumulative increase in interest rates, recent retail trade and other data suggest more persistent excess demand in the economy
- The housing market has seen some pickup
- New construction and real estate listings are lagging demand, which is adding pressure to prices
- In the labour market, there are signs of more availability of workers, but conditions remain tight, and wage growth has been around 4-5%
- Strong population growth from immigration is adding both demand and supply to the economy: newcomers are helping to ease the shortage of workers while also boosting consumer spending and adding to demand for housing
Global economic performance and outlook
- Economic growth has been stronger than expected, especially in the United States, where consumer and business spending has been “surprisingly” resilient
- After a surge in early 2023, China’s economic growth is softening, with slowing exports and ongoing weakness in its property sector
- Growth in the euro area is effectively stalled: while the service sector continues to grow, manufacturing is contracting
- Global financial conditions have tightened, with bond yields up in North America and Europe as major central banks signal further interest rate increases may be needed to combat inflation
- The Bank’s July Monetary Policy Report projects the global economy will grow by “around 2.8% this year and 2.4% in 2024, followed by 2.7% growth in 2025”
Summary and Outlook
As higher interest rates continue to work their way through the economy, the BoC expects economic growth to slow, averaging around 1% through the second half of 2023 and the first half of next year. This implies real GDP growth of 1.8% in 2023 and 1.2% in 2024. The Canadian economy will then move into “modest excess supply” early next year before growth picks up to 2.4% in 2025.
In its July Monetary Policy Report, the Bank noted that CPI inflation is forecast to “hover” around 3% for the next year before gradually declining to 2% in the middle of 2025. This is a slower return to target than was forecast in its January and April projections. As a result, the Bank’s Governing Council remains concerned that progress towards its 2% inflation target “could stall, jeopardizing the return to price stability.”
In terms of what Canadians can expect in the near term, the Bank had this to say: “Quantitative tightening is complementing the restrictive stance of monetary policy and normalizing the Bank’s balance sheet. Governing Council will continue to assess the dynamics of core inflation and the outlook for CPI inflation. In particular, we will be evaluating whether the evolution of excess demand, inflation expectations, wage growth and corporate pricing behaviour are consistent with achieving the 2% inflation target. The Bank remains resolute in its commitment to restoring price stability for Canadians.”
Stay tuned
September 6th, 2023 is the Bank’s next scheduled policy rate announcement. Will there be 1x more increase?
Bank of Canada increases its benchmark interest rate to 4.50%
Today, the Bank of Canada increased its overnight benchmark interest rate 25 basis point to 4.50% from 4.25% in December. This is the eighth time since March 2022 that the Bank has tightened money supply to address inflation.
While the headline increase will certainly make news, it is the Bank’s accompanying commentary on its future moves that will capture the most attention. We summarize the Bank’s observations below, including its forward-looking comments on the potential for future rate increases.
Canadian inflation
- Inflation has declined from 8.1% in June to 6.3% in December, reflecting lower gasoline prices and, more recently, moderating prices for durable goods
- Despite this progress, Canadians are still “feeling the hardship” of high inflation in their essential household expenses, with persistent price increases for food and shelter
- Short-term inflation expectations remain elevated and while year-over-year measures of core inflation are still around 5%, 3-month measures have come down, suggesting that core inflation has “peaked”
Canadian economic and housing market performance
- The Bank estimates Canada’s economy grew by 3.6% in 2022, slightly stronger than was projected in the Bank’s Monetary Policy Report in October, however it projects that growth is expected to “stall through the middle of 2023,” picking up later in the year
- Canadian GDP growth of about 1% is forecast for 2023 and rising to about 2% in 2024, little changed from the Bank’s October outlook
- The economy remains in “excess demand” and the labour market remains “tight” with unemployment near historic lows and businesses reporting ongoing difficulty finding workers
- However, there is “growing evidence” that restrictive monetary policy is slowing activity especially household spending
- Consumption growth has moderated from the first half of 2022 and “housing market activity has declined substantially”
- As the effects of interest rate increases continue to work through the economy, spending on consumer services and business investment is expected to slow
- Weaker foreign demand will likely weigh on Canadian exports
- This overall slowdown in activity will allow supply to “catch up” with demand
Global economic performance and outlook
- The Bank estimates the global economy grew by about 3.5% in 2022, and will slow to about 2% in 2023 and 2.50% in 2024 — a projection that is slightly higher than the Bank’s forecast in October
- Global economic growth is slowing, although it is proving more resilient than was expected at the time of the Bank’s October Monetary Policy Report
- Global inflation remains high and broad-based although inflation is coming down in many countries, largely reflecting lower energy prices as well as improvements in global supply chains
- In the United States and Europe, economies are slowing but proving more resilient than was expected at the time of the Bank’s October Monetary Policy Report
- China’s abrupt lifting of pandemic restrictions has prompted an upward revision to the Bank’s growth forecast for China and “poses an upside risk to commodity prices”
- Russia’s war on Ukraine remains a significant source of uncertainty
- Financial conditions remain restrictive but have eased since October, and the Canadian dollar has been relatively stable against the US dollar
Outlook
Taking all of these factors into account, the Bank decided today’s policy rate increase was necessary and justified.
However, the Bank also offered this important piece of news: “If economic developments evolve broadly in line with (its) outlook, Governing Council expects to hold the policy rate at its current level while it assesses the impact of the cumulative interest rate increases.”
That sounds positive, but as is customary, the Bank also noted that it is prepared to increase the policy rate further if needed to return inflation to its 2% target. It also added the usual language that it “remains resolute in its commitment to restoring price stability for Canadians.”
Although the Bank did not say it, the bottom line is Canadians will have to wait and see what comes next.
Next touch point
March 8, 2023 is the Bank’s next scheduled policy interest rate announcement and we will be on hand to provide an executive summary the same day.
